Water Testing: What Makes Water Good?
We have been learning about the chemical makeup of water and how to test water for hardness, pH, copper and chlorine. We have read and discussed what it means if the water is hard or soft, or if the pH is neutral, alkaline or acidic. Now we are going to consider the question: What makes water good?
In this investigation, your team will conduct and compare several tests on different water samples to try to determine what makes each water sample “good” and which one is the best for you to drink, to wash with, etc. Use your data to draw your conclusions.
Approximately five 45-minute class sessions, including four lead-up activities to learn how to do each water test.
Instructional Support Downloads
Task Menu Quick Links
Exemplars Rubrics
In this investigation, students need to list materials used, conduct the four tests and record their data for two water samples (tap water and bottled water). Then, students should be able to write an explanation for which water sample they think is better, based on the data they collected.
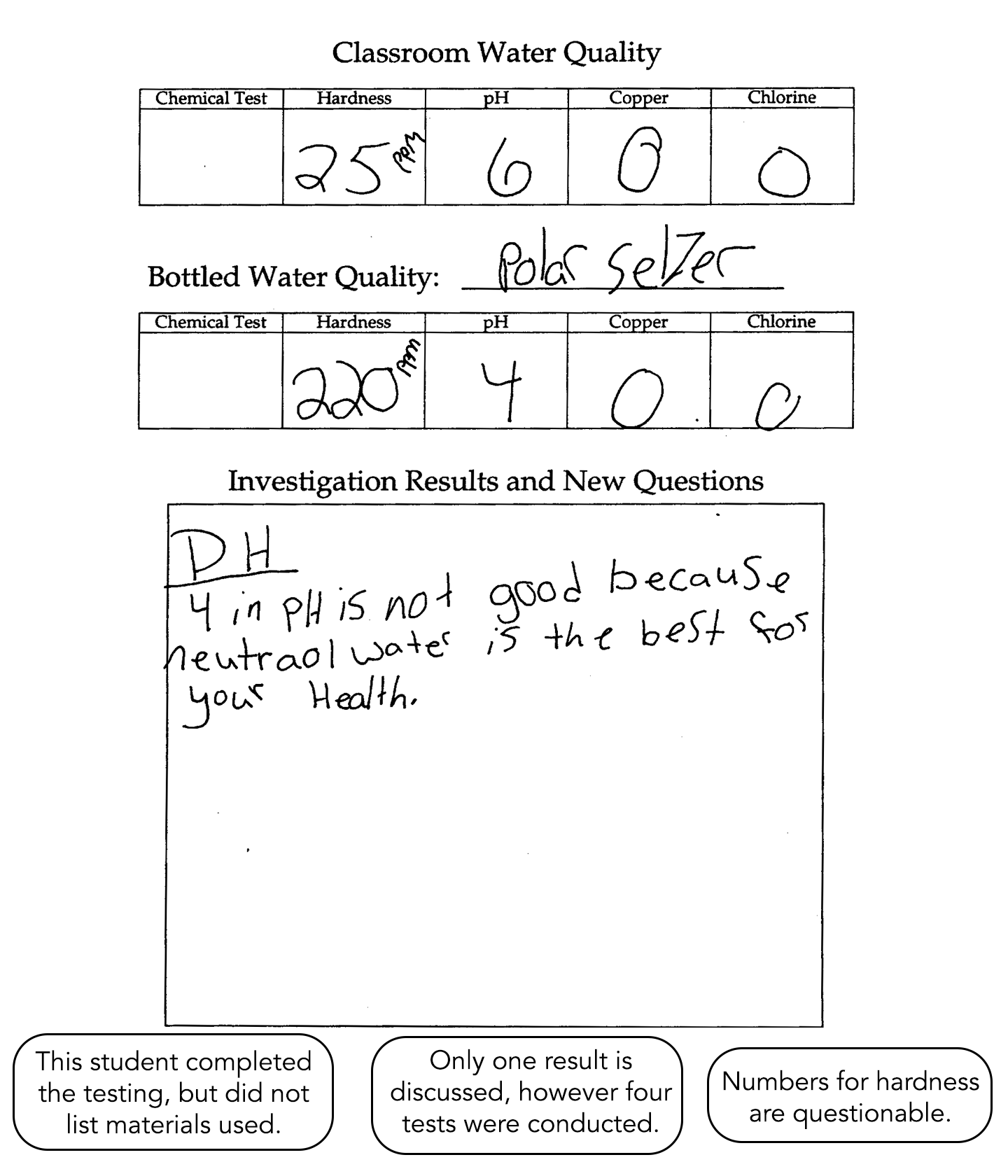
This student completes the testing but fails to list the materials used. Only one result is discussed, but four tests are conducted. The numbers for hardness are questionable. There is little evidence of conceptual understanding.
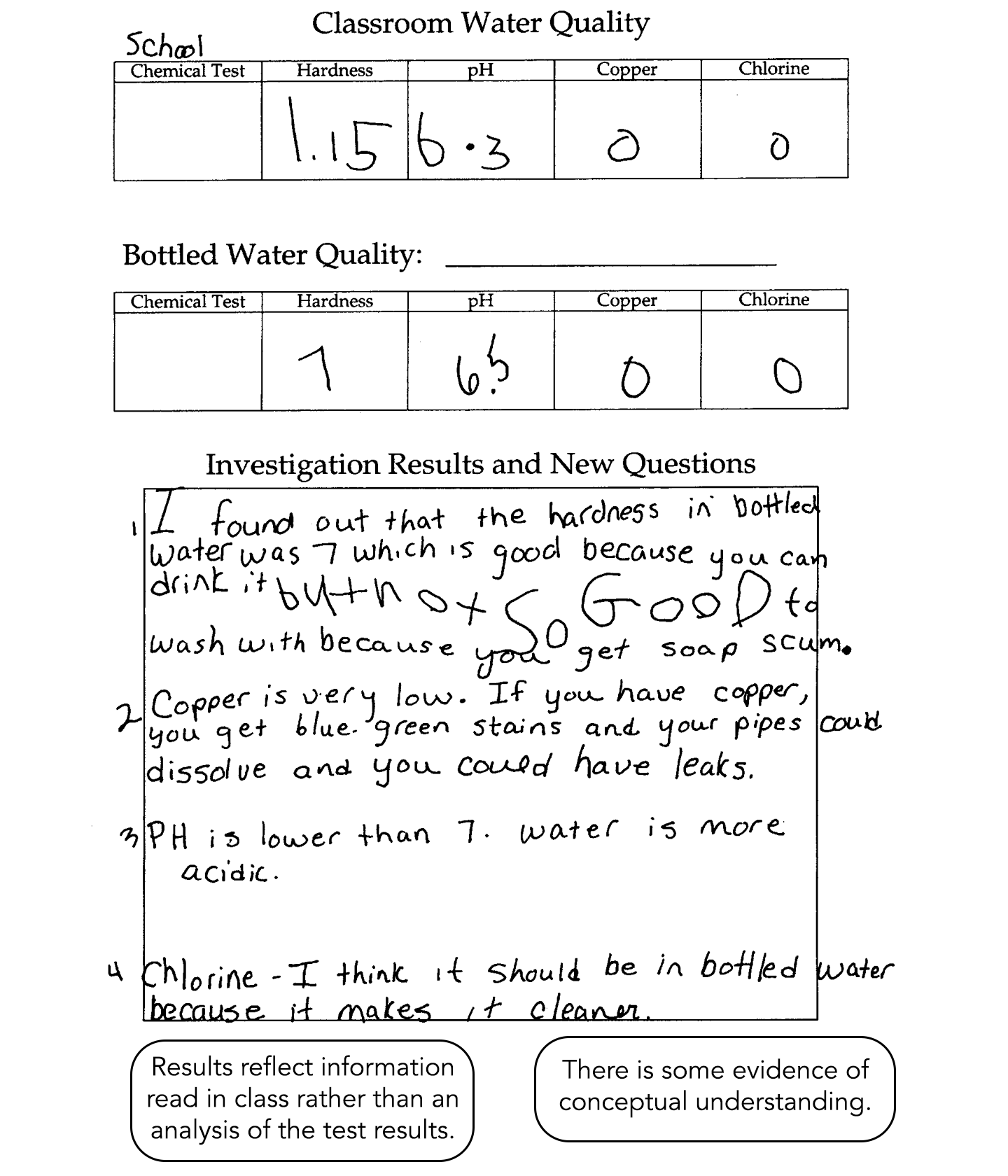
This student completes the testing and lists the materials used. Results reflect information read in class rather than an analysis of the test results or comparisons between the two samples. There is some evidence of conceptual understanding.
This student includes a list of materials used and collects all of the data from the four tests. The discussion of results compares each quality tested and demonstrates conceptual understanding that builds on prior knowledge and experience.
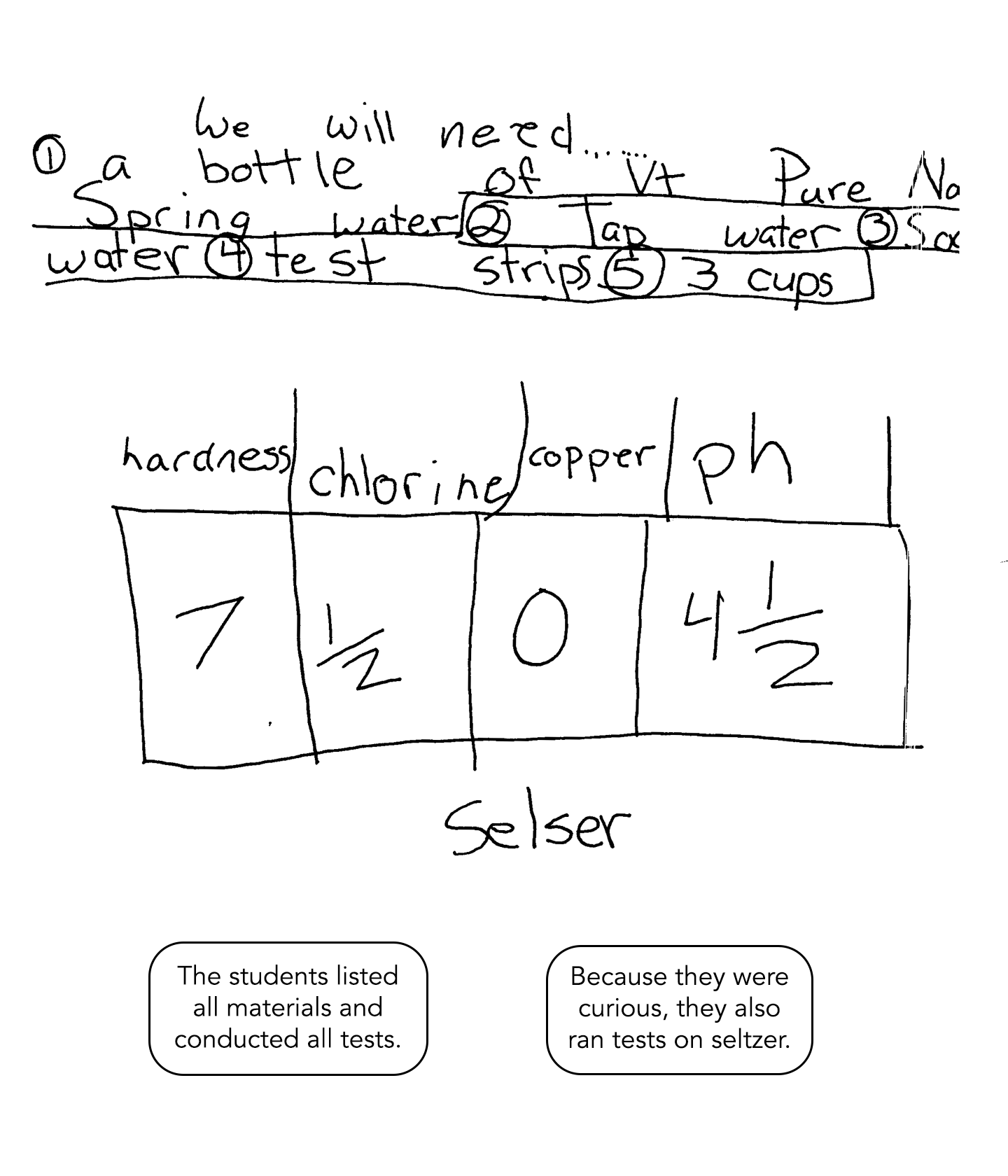
This solution includes a list of materials and data from all tests conducted. Because the students are curious, they also test seltzer – extending thinking beyond earlier investigations. The discussion of results include information learned in class, information learned through the testing, and comparisons of the data. There is clear evidence of conceptual understanding.